Gmail and Outlook dominate the email landscape, but their delivery performance and filtering systems differ significantly. Here’s what you need to know:
- Gmail: Better inbox placement rates (53.70% in Q1 2025), AI-driven spam filtering, strict sender reputation standards, and mandatory SPF, DKIM, and DMARC authentication for all senders.
- Outlook: Lower inbox placement rates (26.77% in Q1 2025), heuristic spam filtering, variable sender requirements based on email volume, and more user-controlled filtering options.
Key Takeaways:
- Gmail offers more consistent inbox placement and rewards engagement but has stricter spam complaint thresholds (0.3%).
- Outlook provides flexibility for smaller senders but struggles with consistent delivery and has higher filtering sensitivity.
Quick Comparison:
| Aspect | Gmail | Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| Inbox Placement | 53.70% (Q1 2025) | 26.77% (Q1 2025) |
| Spam Filtering | AI-driven | Heuristic + user control |
| Authentication | SPF, DKIM, DMARC required | Required for >5,000/day senders |
| Spam Complaint Tolerance | <0.3% | Not specified |
| Tools | Postmaster Tools | SNDS, JMRP |
Conclusion: Gmail is generally better for marketers prioritizing inbox placement and engagement, while Outlook suits businesses reliant on Microsoft’s ecosystem but requires more technical setup.
Outlook vs Gmail: Which Is Better For Cold Email? (2025)
Inbox Placement Rates: Gmail vs Outlook
For email marketers, understanding inbox placement rates is essential. While delivery rates show whether an email was accepted by the server, inbox placement rates reveal whether it landed in the primary inbox – key information for campaign success.
Recent data highlights a decline in email deliverability in Q1 2025 compared to Q1 2024, with Microsoft services seeing the sharpest drops. Interestingly, the focus has shifted from message content to sender reputation as the primary factor influencing inbox placement.
Gmail Inbox Placement Performance
In Q1 2025, Gmail’s average inbox rate fell to 53.70%, down from 58.72% in Q1 2024. Google Workspace saw a similar trend, with an inbox rate of 53.36%, representing a 10.49% decline from the previous year.
Despite these decreases, Gmail’s filtering system is known for being “smart but fair”. It uses advanced algorithms to evaluate sender reputation and domain authenticity. Gmail enforces strict standards but rewards positive practices. For instance, the platform maintains a spam complaint rate threshold of 0.3% and expects marketers to achieve over 90% inbox rates to meet its stringent requirements. High open and reply rates can quickly improve sender reputation, as Gmail is highly responsive to engagement signals.
Outlook Inbox Placement Performance
Outlook and other Microsoft email services pose even greater challenges for marketers. In Q1 2025, Outlook/Hotmail’s average inbox rate plummeted to 26.77%, a steep drop from 49.33% in Q1 2024 – an alarming 22.56% decline. Exchange (Office365) also experienced a significant decrease, with inbox rates falling from 77.43% to 50.70% – a 26.73% drop.
Microsoft’s stricter filtering approach often flags emails, even when senders adhere to best practices. The platform’s filters can blacklist domains without warning, especially for high-volume senders. Additionally, Microsoft’s spam filters are known to misclassify legitimate emails, further complicating deliverability. Unlike Gmail, Outlook’s limited engagement tracking makes it harder for marketers to build a strong sender reputation.
Comparison Table: Gmail vs Outlook Inbox Placement Rates
| Inbox Provider | Average Inbox Rate (%), Q1 2024 | Average Inbox Rate (%), Q1 2025 | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gmail | 58.72 | 53.70 | -5.02 |
| Google Workspace | 63.85 | 53.36 | -10.49 |
| Outlook/Hotmail | 49.33 | 26.77 | -22.56 |
| Exchange (Office365) | 77.43 | 50.70 | -26.73 |
The numbers clearly show Gmail outperforming Outlook in inbox placement rates. Gmail consistently maintained over 50% inbox placement, while Outlook/Hotmail dropped to just 26.77%. Even with its steeper decline, Google Workspace still achieved nearly double the inbox rate of Outlook/Hotmail. These differences highlight the importance of tailoring strategies to each platform.
The implications for businesses are significant. Research shows that nearly 33% of recipients feel disappointed when marketing emails land in spam, and 10% lose trust in the brand as a result. With Outlook’s lower inbox placement rates, marketers risk damaging customer relationships and missing revenue opportunities.
While both platforms present challenges – given the industry benchmark of 90% inbox placement – Gmail’s more predictable filtering system and better performance make it a preferred choice for businesses seeking reliable inbox access over integration with the Microsoft ecosystem.
Spam Filtering Methods and Policy Differences
Understanding how Gmail and Outlook filter emails is crucial for marketers aiming to avoid the spam folder and connect with their audience. Both platforms work hard to shield users from unwanted messages, but their methods differ substantially. With spam making up 84.3% of all email traffic in 2023, these systems are constantly at work to maintain clean inboxes.
Both Gmail and Outlook use multiple checks to decide what to do with an email after accepting it. These checks determine whether an email lands in the inbox, gets sent to the spam folder, or is outright rejected. The way each platform handles these steps highlights the differences in their approaches.
Gmail Spam Filtering Methods
Gmail relies heavily on AI-driven spam filtering, blocking over 99.9% of threats before they reach users’ inboxes. Its adaptive algorithms learn from user behavior, analyzing how emails are handled to improve filtering accuracy. Gmail also prioritizes email delivery based on perceived importance. Emails are categorized into Primary, Promotions, or Spam folders based on user feedback, content analysis, and sender authentication. When users mark emails as spam or move them to different folders, Gmail adjusts its algorithms accordingly.
For bulk senders, Gmail has strict rules. It enforces a 0.1% spam rate cap, meaning if more than 0.1% of recipients mark your emails as spam, your sender reputation takes a hit. Additionally, Gmail requires bulk senders to use SPF, DKIM, and DMARC authentication, making these protocols non-negotiable for successful delivery.
Outlook Spam Filtering Methods
Microsoft’s Outlook uses a mix of machine learning and customizable policies to filter spam. It focuses on verifying the sender’s identity, flagging malicious emails as junk, and marking suspicious but less harmful messages as “unverified”. Unlike Gmail’s AI-heavy approach, Outlook offers more user control, allowing customization through tools like Safe Senders Lists and manual filtering settings. It also uses quarantine policies to handle suspected spam, giving users greater flexibility in managing their inboxes.
Outlook doesn’t impose a specific spam rate cap but evaluates emails based on their content. That said, Microsoft also recommends SPF, DKIM, and DMARC authentication, and using these protocols can greatly improve delivery success. These differences in filtering strategies contribute to the variations in how emails are handled across the two platforms.
Comparison Table: Spam Filters and Triggers
| Feature | Gmail | Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Detection Method | AI-driven language models | Heuristic analysis and feedback |
| Authentication Requirements | SPF, DKIM, DMARC required | SPF, DKIM, DMARC recommended |
| Spam Rate Tolerance | 0.1% spam rate cap for bulk emails | No explicit rate cap (content-focused) |
| User Control | Limited customization | Extensive user-defined policies |
| Sender Verification | Reputation-based scoring | Verified/Unverified sender marking |
| Content Analysis | AI content evaluation | Heuristic content analysis |
The main distinction lies in their filtering philosophies. Gmail relies on AI-driven models that dynamically adapt to patterns, while Outlook uses rule-based heuristic analysis combined with user feedback. Gmail’s system is more automated and learns from behavior, whereas Outlook offers more manual control to the user.
Both platforms, however, share common spam triggers. To avoid being flagged, senders should steer clear of spammy language, refrain from using all caps in subject lines, avoid linking to unsecured websites, and always include an unsubscribe option. Failure to follow proper authentication protocols also increases the likelihood of emails being marked as spam.
For marketers, the authentication requirements highlight a practical difference. Gmail’s mandatory SPF, DKIM, and DMARC setup for bulk senders makes proper configuration essential for good delivery rates. Outlook, while more lenient, still rewards authenticated emails with better placement.
These differences explain why inbox placement rates can vary between the two platforms. Gmail’s strict but predictable AI-driven system rewards adherence to best practices, while Outlook’s more flexible, user-influenced approach can lead to less consistent results.
sbb-itb-eece389
Sender Reputation and Authentication Requirements
Your sender reputation works like a credit score, but for email delivery. Gmail and Outlook evaluate this reputation differently, which directly affects whether your emails land in the inbox or get caught in spam filters. Understanding these distinctions allows you to fine-tune your approach for each platform. Let’s break down how each platform incorporates authentication into reputation management.
Gmail Sender Reputation Management
Gmail takes a detailed approach to sender reputation, closely linking it with your DNS configuration. To meet Gmail’s standards, your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records need to work in harmony.
The platform has strict spam tolerance, requiring spam rates to stay below 0.3% – that’s fewer than 3 complaints per 1,000 recipients. Anything higher can harm your reputation. Gmail also insists on a DKIM key length of at least 1,024 bits for stronger encryption.
Another key requirement is DMARC alignment, which ensures the domain in your “From:” header matches the domain used in your SPF or DKIM records. This alignment helps prevent spoofing and builds trust with Gmail’s systems. Beyond technical measures, Gmail rewards user engagement – emails that recipients open, reply to, or mark as “not spam” positively impact your reputation.
To help you monitor your performance, Gmail offers Postmaster Tools. This free resource provides insights into spam rates, reputation status, and delivery errors, giving you actionable data to improve your email campaigns.
Gmail’s strict requirement for synchronized SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records highlights its high standards for sender reputation.
Outlook Sender Reputation Management
Outlook takes a different approach, tailoring its requirements based on email volume and engagement patterns.
For high-volume senders – those sending over 5,000 emails per day – Outlook requires SPF, DKIM, and DMARC compliance. Smaller senders have more flexibility, but meeting these standards can still improve delivery rates.
Outlook uses scoring systems like the Spam Confidence Level (SCL) and Bulk Complaint Level (BCL) to evaluate emails. These scores consider factors like sender authentication, content quality, and how recipients interact with your messages.
Microsoft also stresses the importance of using accurate “From” and “Reply-To” addresses that match your sending domain. While this is crucial for high-volume senders, it benefits all senders by improving trust and deliverability.
“Email is still a key tool for personal and business communication. So, Outlook is working hard to protect inboxes and maintain trust in our digital world.” – Microsoft Tech Community
Engagement is another critical factor for Outlook. Sending emails only to recipients who want them and promptly honoring unsubscribe requests are essential for maintaining a good reputation.
Outlook provides Smart Network Data Services (SNDS) to help you track your sender reputation. While not as detailed as Gmail’s Postmaster Tools, SNDS offers insights into your IP reputation, complaint rates, and delivery statistics. Additionally, PTR records (reverse DNS) are crucial for Outlook, as they help verify your server’s legitimacy.
Comparing Gmail and Outlook Requirements
Gmail enforces strict, universal standards for all senders, while Outlook adjusts its requirements based on email volume. Despite these differences, both platforms emphasize the importance of proper authentication for better inbox placement. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Authentication Requirement | Gmail | Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| SPF Authentication | Mandatory (All Senders) | Mandatory (Bulk Senders >5,000/day) |
| DKIM Authentication | Mandatory (All Senders) | Mandatory (Bulk Senders >5,000/day) |
| DMARC Implementation | Required for Bulk (p=none OK) | Required for Bulk (p=none OK) |
| DKIM Key Length | 1,024 bits minimum | Not specified |
| Spam Complaint Rate | Must be <0.3% | Not specified |
| PTR Records | Required (All Senders) | Recommended |
Both Gmail and Outlook accept DMARC policies set to p=none, which allows monitoring your domain without rejecting emails. However, the ultimate goal should be a p=reject policy to fully protect your domain from spoofing attempts.
“The end goal is ideally a policy of p=reject. That’s what DMARC is for. Ensuring that your domain cannot be spoofed and protecting our mutual customers from abuse.” – Marcel Becker, Senior Director of Product at Yahoo
Regularly monitoring your authentication setup is key to avoiding reputation damage. Both platforms expect you to maintain clean email lists, handle bounces properly, and offer easy unsubscribe options. By combining these foundational practices with proper authentication, you can improve email delivery and build trust across both Gmail and Outlook.
Email Delivery Optimization Tips for Gmail and Outlook
When it comes to navigating the distinct filtering systems of Gmail and Outlook, a one-size-fits-all approach simply doesn’t work. Each platform has its own set of rules and quirks, making targeted strategies essential. With 16% of marketing emails failing to land in inboxes in 2024, understanding these platform-specific nuances is critical for US marketers aiming to improve email performance.
Gmail Delivery Optimization Tips
Gmail’s filtering system is heavily tied to sender reputation, and it’s all about engagement. With a strict spam complaint threshold of 0.3%, every recipient interaction matters. Positive actions like opens, clicks, and forwards help boost your reputation, while spam complaints and unsubscribes can drag it down.
Here’s how to improve Gmail delivery:
- Personalize your content: Tailor emails to your audience to encourage engagement.
- Switch things up: Rotate templates and subject lines to avoid Gmail’s content fingerprinting.
- Clean your lists: Remove inactive subscribers after 90–120 days to maintain a healthy list.
- Timing matters: Avoid sending emails during peak server times (top, half, and bottom of each hour).
- Keep it light: Ensure your email’s HTML size stays under 102 KB to prevent delivery issues.
For less engaged subscribers, run re-engagement campaigns with monthly promotions. If they remain inactive after a year, implement a sunset policy to phase them out.
“Everyone’s goal is obviously 100%. What we focus on is our inbox placement. We want 100% of our emails getting to the inbox, and if it drops below 90%, we’re going to immediately investigate what’s going on.” – Carin Slater, Manager of Lifecycle Email Marketing at Litmus
Outlook Delivery Optimization Tips
Outlook’s filtering system relies on scoring mechanisms like the Spam Confidence Level (SCL) and Bulk Complaint Level (BCL). Microsoft is quick to block emails when issues arise, and recovering from a poor reputation can take time. Consistency is key here.
To improve your Outlook delivery:
- Authenticate your emails: Use SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to build trust – especially crucial for high-volume senders (over 5,000 emails daily).
- Watch your language: Avoid spammy words and maintain a balanced text-to-image ratio.
- Stay on top of bounces: Remove hard bounces promptly to keep your list clean.
- Make unsubscribing easy: A clear unsubscribe option reduces complaints.
- Monitor performance: Use tools like Smart Network Data Services (SNDS) and the Junk Mail Reporting Program (JMRP).
- Warm up new IPs: Gradually increase sending volume to establish a positive reputation.
For marketers juggling these challenges, specialized tools can make all the difference.
How MailMonitor Improves Email Delivery
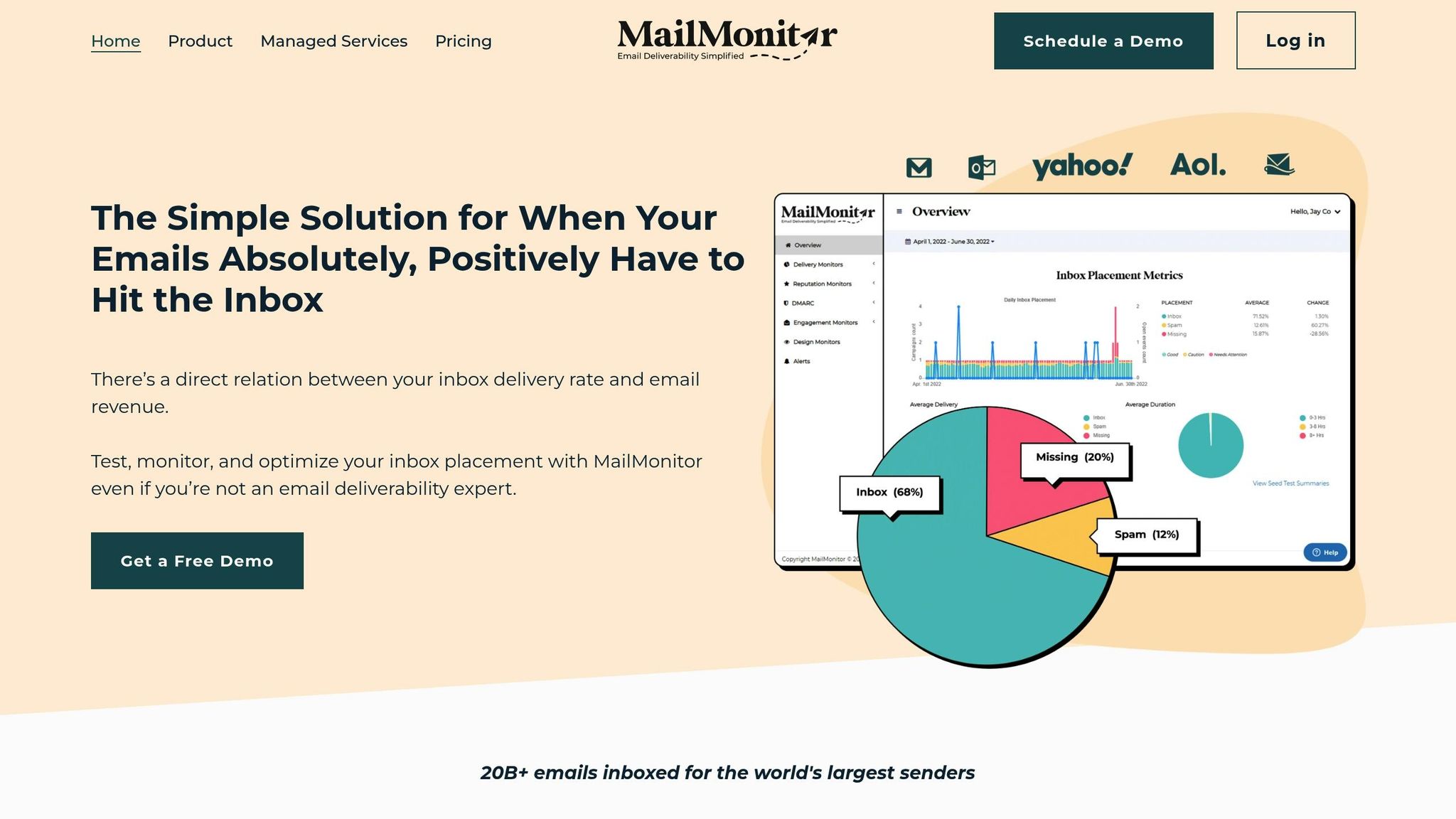
MailMonitor offers tools designed to tackle the unique challenges of Gmail and Outlook, helping marketers optimize deliverability with precision.
- Inbox Placement Testing: This feature provides real-time insights into where your emails land – whether it’s the inbox, promotions tab, or spam folder. Seed testing helps pinpoint platform-specific issues quickly.
- Reputation Monitoring: By consolidating Gmail’s Postmaster Tools and Outlook’s SNDS data, MailMonitor offers actionable insights. Alerts notify you when reputation scores dip below ideal levels, allowing for immediate action.
- Email Verification: Keep your email lists clean by identifying invalid addresses, spam traps, and inactive accounts before sending. This is crucial since 70% of emails have at least one spam-related issue that could block delivery.
MailMonitor also offers custom alerts for delivery problems and Managed Services that include IP warm-up assistance, blocklist removal, and ongoing consultation. These tools ensure your email campaigns meet the specific requirements of each platform while maintaining strong performance metrics.
Gmail vs Outlook: Final Comparison Summary
Choosing between Gmail and Outlook boils down to your specific needs and technical expertise. For US marketers, Gmail tends to outperform Outlook in inbox placement and overall deliverability. On the other hand, Outlook offers advanced features but demands a more technical setup to achieve consistent results.
Currently, the average email deliverability rate stands at 83.1%, meaning 16.9% of emails fail to reach their destination. This highlights the importance of tailoring strategies to each platform for the best results.
| Aspect | Gmail | Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| Inbox Placement | Generally better performance | Inconsistent performance |
| Spam Filtering | Machine learning-based, strict | Proprietary system, more stringent |
| Setup Complexity | Easy to set up | More complex and technical |
| Authentication | Requires SPF, DKIM, and DMARC | Requires SPF, DKIM, and DMARC |
| Reputation Management | Uses a Sender Reputation Score | Uses Sender Score Certification |
For most US marketers, Gmail is the go-to option thanks to its reliable deliverability, advanced machine learning filters, and user-friendly setup. Gmail’s spam complaint threshold is set at 0.3%, which is manageable with proper list hygiene and engagement tactics. Meanwhile, Outlook is a better fit for organizations heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem, particularly those using Microsoft 365, but it demands strict compliance with authentication protocols to maintain deliverability.
To maximize success, focus on platform-specific strategies. Gmail users should lean into personalization and content variety to boost engagement. Outlook users, however, need to prioritize strong technical authentication and consistent sending habits. Regardless of the platform, maintaining clean mailing lists is critical.
As deliverability standards continue to evolve, regular monitoring is key. Tools like MailMonitor can help you track inbox placement and reputation, ensuring your emails consistently reach their intended audience.
FAQs
How do Gmail and Outlook differ in their spam filtering, and what does this mean for email deliverability?
Gmail and Outlook handle spam filtering in their own distinct ways, and these differences can have a big impact on email deliverability. Gmail’s filtering system is known for being advanced and constantly evolving. This helps it accurately identify spam while still allowing legitimate emails to land in the inbox. The result? Fewer emails wrongly flagged as spam and a better chance of your messages reaching their intended audience.
Outlook, however, takes a stricter, more cautious approach. While this can be effective in blocking spam, it sometimes leads to legitimate emails – like cold outreach or marketing messages – being misclassified or even blocked. This can cause higher bounce rates and make it tougher to ensure your emails get through.
To navigate these differences, focus on strategies that work for both platforms. Build a strong sender reputation, use proper email authentication methods like SPF and DKIM, and always prioritize sending relevant, high-quality content. These steps can help improve your chances of successful email delivery, no matter the platform.
What steps can marketers take to improve their sender reputation and boost email deliverability on Gmail and Outlook?
To boost your sender reputation and improve email deliverability on platforms like Gmail and Outlook, start by keeping a clean email list. Regularly remove invalid or inactive email addresses to cut down on bounce rates. This simple step can go a long way in ensuring your emails reach the intended inboxes.
Another key factor is maintaining consistent sending patterns. Sending emails at predictable volumes and encouraging high engagement – such as opens and clicks – helps build credibility with email providers. Engagement signals show that recipients value your content, which in turn boosts trust.
Don’t skip email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. These tools confirm your identity as the sender, reducing the chances of your emails being flagged as spam. Not only do they improve inbox placement, but they also strengthen your reputation as a reliable sender.
Lastly, stay aligned with Gmail and Outlook’s guidelines and keep a close eye on performance metrics. This proactive approach can help fine-tune your strategy and maximize your email delivery success.
What challenges make it harder to maintain high inbox placement rates on Outlook compared to Gmail, and how can these be resolved?
Maintaining solid inbox placement rates on Outlook can be trickier than on Gmail. Why? Outlook has stricter spam filters and tougher requirements for sender reputation. This often results in higher spam rejection rates, meaning your emails are more likely to get flagged or blocked.
To navigate these hurdles, focus on building a reliable sender reputation by following these practices:
- Steer clear of spammy language and questionable content.
- Regularly clean your email list by removing invalid or inactive addresses.
- Authenticate your emails using SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols.
It’s also important to keep an eye on engagement metrics like open rates and click-through rates. Outlook is particularly sensitive to sudden spikes in email volume, so maintaining a consistent sending pattern is crucial. Proactive list management and steady engagement efforts can go a long way in boosting your email deliverability on this platform.


